Mergify Configuration File
Everything you need to know about Mergify configuration file
The Mergify configuration file is an essential component of using our platform effectively. This document will provide a comprehensive overview of the file, including its name, format, and the data structure schema.
Configuration File Name
Section titled Configuration File NameMergify applies the following rule to find and use its configuration:
-
It reads the file named
.mergify.yml, or, as a fallback,.mergify/config.ymlor.github/mergify.ymlfrom the repository root directory. -
It reads the file from the default repository branch configured on GitHub — usually
main. -
It can extends the configuration by another configuration using the keyword
extends— see “extending the configuration file”.
File Format
Section titled File FormatThe configuration file uses the YAML format, which is both human-readable and machine-parsable. YAML is easy to read and edit, making it a popular choice for configuration files.
The file main type is a dictionary and each key of the dictionary configures a different aspect of Mergify:
-
pull_request_rulesconfigures Automation Workflow; -
merge_protectionsandmerge_protections_settingsconfigures Merge Protections; -
queue_rulesconfigures the Merge Queue; -
merge_queueconfigures option for the Merge Queue; -
priority_rulesconfigures the priorities for the Merge Queue; -
commands_restrictionsconfigures who is able to run commands; -
defaultsallows to configure default options for various actions; -
sharedallows to define any YAML payload that can be used using YAML anchors; -
extendsallows to extend the configuration file by importing another configuration file.
Pull Request Rules
Section titled Pull Request RulesThe top-level key pull_request_rules allows to automate your workflow by
writing rules that execute actions. It must be a list of dictionary with the
following keys:
| Key name | Value type | |
|---|---|---|
actions | Actions | |
The actions to perform when the rule matches. | ||
conditions | List of conditions | |
The conditions that must be met for the rule to be evaluated. | ||
description | string or null | |
A description of the rule. | ||
disabled | DisabledDict null | |
If the rule is disabled, the reason why it's disabled. | ||
name | string | |
The name of the rule. This is used when reporting information about a rule. It's not possible to have two rules with the same name. | ||
Example:
pull_request_rules:
- name: add label when author is jd
description: jd needs his own label because reasons
conditions:
- author = jd
actions:
label:
add:
- jdMerge Protections
Section titled Merge ProtectionsThe top-level key merge_protections allows to protect your merge by adding a
list of rules that must match before allowing the pull request to be merged.
| Key name | Value type | |
|---|---|---|
description | string or null | |
A description of the rule | ||
if | List of conditions | |
The conditions to check before applying the rule | ||
name | string | |
The name of the rule | ||
success_conditions | List of conditions | |
The conditions to check to validate the rule | ||
The top-level key merge_protections_settings allows to configure the
behavior of Merge Protections
| Key name | Value type | Default | |
|---|---|---|---|
post_comment | boolean | | |
Whether to post merge protection status comments on pull requests | |||
reporting_method | check-runs or deployments | | |
The merge protection reporting method | |||
Merge Queue
Section titled Merge QueueThe top-level key merge_queue allows to configure certain aspect of the merge
merge queue.
| Key name | Value type | Default | |
|---|---|---|---|
dequeued_label | string or null | | |
The label to add on pull requests when they are removed from the merge queue. | |||
max_parallel_checks | integer | | |
The maximum number of speculative checks allowed to run at the same time. Setting this value to 1 disables speculative checks. | |||
mode | serial or parallel | | |
Defines how the merge queue schedules pull requests.
| |||
queued_label | string or null | | |
The label to add on pull requests when they are added to the merge queue. | |||
reset_on_external_merge | never or always | | |
Defines the behavior of the merge queue when something is merged outside of the queue. "always": The queue is reset when an external merge is detected. All queued pull requests are re-evaluated to ensure correctness based on the new base branch state. "never": The queue remains unchanged. It does not reset or re-evaluate based on the external merge. | |||
skip_intermediate_results | boolean | | |
Allow PRs to merge even if their own speculative check fails, as long as a later downstream check including them passes and schedule conditions are valid. | |||
status_comments | all, outcomes or none | | |
Controls the level of status comments posted on pull requests in the queue.
| |||
Queue Rules
Section titled Queue RulesThe top-level key queue_rules allows to define the rules that reign over your
merge queue.
| Key name | Value type | Default | |
|---|---|---|---|
allow_inplace_checks | boolean | | deprecated |
Deprecated: this value is computed automatically. In-place checks are enabled only when:
| |||
allow_queue_branch_edit | boolean | | |
When creating a branch for a queue, if the commits of this branch are edited by an entity external to Mergify, Mergify dequeues all pull requests embarked in the branch and report the issue as a failure. If set to | |||
autoqueue | boolean | | |
When set to true, automatically add a pull request to the queue when it matches the queue conditions. When false, the pull request must be manually queued. | |||
batch_max_failure_resolution_attempts | integer or null | | |
The number of attempts to resolve a batch failure before dequeueing pull requests. By default, Mergify will attempt to resolve a batch failure by splitting the batch multiple times until it finds the root cause of the failure. You can stop this process earlier by limiting the number of resolution attempts. Setting this to 0 will dequeue all the pull requests from a batch when a batch fails. | |||
batch_max_wait_time | duration | | |
The maximum amount of time to wait for additional pull requests before processing a batch that hasn't reached | |||
batch_size | integer | | |
The maximum number of pull requests per speculative check in the queue. Must be between 1 and 128. | |||
branch_protection_injection_mode | queue, merge or none | | |
Branch protections conditions injection mode to use.
| |||
checks_timeout | duration or null | | |
The amount of time the merge queue waits for pending checks to return before dequeueing pull requests. This cannot be less than 60 seconds. | |||
commit_message_template | template or null | | |
Template to use as the commit message when using the merge or squash merge method. | |||
draft_bot_account | template or null | | |
Mergify can impersonate a GitHub user to create its draft pull requests. If no | |||
max_check_retries | integer | | |
The maximum number of retries allowed to be executed on failed PRs or batches before proceeding with the normal failure resolution process. | |||
merge_bot_account | template or null | | |
Mergify can impersonate a GitHub user to merge pull requests. If no | |||
merge_conditions | List of conditions | ||
The list of conditions to match to get the queued pull request merged. In case of draft pull request, the merge conditions for checks are evaluated against the temporary pull request instead of the original one. | |||
merge_method | merge, rebase, squash or fast-forward or null | | |
Merge method to use. If no value is set, Mergify uses the first authorized method available in the repository configuration. | |||
name | string | ||
queue_branch_merge_method | fast-forward or null | | |
If set to | |||
queue_branch_prefix | template | | |
Prefix for the merge queue branch name | |||
queue_conditions | List of conditions | ||
The list of conditions that needs to match to queue the pull request. | |||
update_bot_account | template or null | | |
For certain actions, such as rebasing branches, Mergify has to impersonate a GitHub user. You can specify the account to use with this option. If no | |||
update_method | rebase or merge or null | | |
Method to use to update the pull request with its base branch when the check is done in place. Possible values:
When | |||
Priority Rules
Section titled Priority RulesThe top-level key priority rules allows to define the rules that will determine
which priority a pull request has when entering your merge queue.
| Key name | Value type | Default | |
|---|---|---|---|
allow_checks_interruption | boolean | | |
Allow interrupting the ongoing checks when the pull request entering the queue has a higher priority than the queued one(s). If set to false, a pull request with higher priority will be inserted just after the pull requests that have checks running. | |||
conditions | List of conditions | ||
The list of conditions that needs to match to assign priority to the pull request. | |||
name | string | ||
Name of the rule. | |||
priority | high, medium or low or integer | | |
The priority of the pull request. | |||
Defaults
Section titled DefaultsThe defaults section provides a means to set configuration values that act as
fallbacks for:
- Actions executed by both pull request rules and commands
- Configuration options for queue rules
Instead of defining the same options repeatedly for different rules, you can specify
them once in the defaults section. If a particular option is directly defined under
pull_request_rules or queue_rules, it will take precedence; otherwise, the system
resorts to the values defined in the defaults section.
defaults:
actions:
comment:
bot_account: Autobot
queue_rule:
batch_size: 10
pull_request_rules:
- name: comment with default
conditions:
- label = comment
actions:
comment:
message: I 💙 Mergify
queue_rules:
- name: default
- name: default with smaller batch
batch_size: 2This configuration is equivalent to:
pull_request_rules:
- name: comment with default
conditions:
- label = comment
actions:
comment:
message: I 💙 Mergify
bot_account: Autobot
queue_rules:
- name: default
batch_size: 10
- name: default with smaller batch
batch_size: 2In the example, the bot_account value is taken from the defaults section,
simplifying the pull_request_rules and ensuring consistent behavior across
different rules.
The same behavior applies for the batch_size option of the queue_rules, the
default value of 10 gets applied to the queue rule default but not for the
queue rule default with smaller batch, because it already has batch_size: 2.
Shared
Section titled SharedYou can store anything in the shared key. Its main purpose is to provide a
place to put redundant YAML anchors. See
Sharing.
Extends
Section titled ExtendsMergify offers a feature to extend your configuration file by incorporating
settings from another repository, aiding in consistency and reducing
duplication. This is achieved by using the extends keyword at the top of your
configuration file and specifying the source repository. See Extending
Configuration Files.
JSON Schema Specification
Section titled JSON Schema SpecificationFor those interested in a more detailed and machine-readable description of the Mergify configuration file format, a JSON Schema specification is available. This specification can help you understand the structure of the configuration file and can be used to generate client libraries, server stubs, or API documentation.
You can find the JSON Schema specification for the Mergify configuration here .
Validation and Troubleshooting
Section titled Validation and TroubleshootingWhen working with Mergify’s configuration file, it’s essential to validate and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Ensuring that your configuration file is error-free and well-structured can help prevent unexpected behavior and maintain a smooth workflow.
Validation
Section titled ValidationTo validate your Mergify configuration file, you can use Mergify’s built-in validation tool. Whenever you push a change to the configuration file, Mergify will automatically validate the configuration and report any errors or warnings in the “Checks” tab of your pull request.
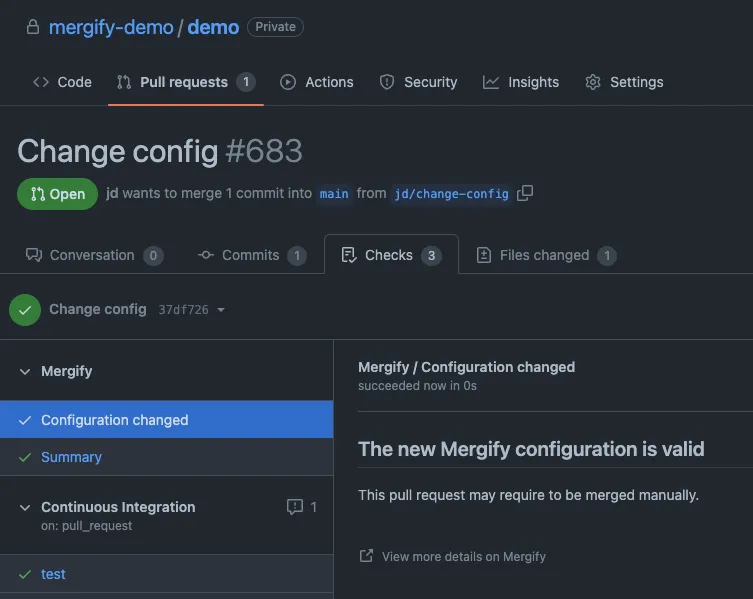
If there are any issues with your configuration file, you will receive a detailed description of the problem and guidance on how to fix it. Be sure to address any errors or warnings to ensure optimal performance and avoid potential issues.
Validate Locally With Pre-Commit
Section titled Validate Locally With Pre-CommitTo catch issues before pushing, you can validate your configuration locally
using Mergify’s pre-commit hook. Add this to your .pre-commit-config.yaml:
repos:
- repo: https://github.com/Mergifyio/mergify-pre-commit
rev: 1.0.0
hooks:
- id: validate-mergify-configTroubleshooting
Section titled TroubleshootingIf you encounter issues or unexpected behavior with your Mergify configuration file, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
-
Double-check the file name and location: ensure that your configuration file is correctly named (e.g.,
.mergify.yml) and is located in the right place. See Configuration File Name for details. -
Verify the YAML syntax: confirm that your configuration file follows the proper YAML syntax, including correct indentation, spacing, and structure.
-
Review your rules and conditions: Make sure that your rules and conditions are correctly defined and accurately reflect your intended workflow.
-
Check for conflicting rules: examine your rules for any conflicts or overlapping conditions that could cause unintended behavior.
-
Consult Mergify’s documentation: refer to Mergify’s documentation for guidance on creating and managing your configuration file, as well as understanding the various features and options available to you.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can effectively identify and resolve any issues with your Mergify configuration file, ensuring a smooth and efficient automation process for your repository.